Day of the Lesson:
- Students will work in teams of 3 to 4. Please give thought to student groupings before the class visit.
- If possible, we would like to use your computer to share a Google Slides presentation that we will email ahead of time.
- Have your students clear everything off their desks before the lesson begins.
- Students will need a pencil to work through a worksheet.
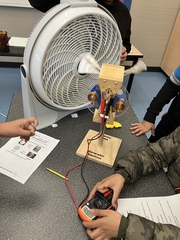
- The lesson requires the use of several fans. The educator will bring power strips but please make outlets available during the lesson.
- Please do not leave your classroom while the educator is teaching.
- The educator may arrive at your classroom 20-30 minutes early to set up materials.
Pre-lesson Self-Guided Slides Series: Where does our electricity come from?
This 5 lesson series will give your students the background information about the energy sources needed to generate our electricity and the connection to global warming. These links are interactive Google Slide presentations that, when opened, will ask you to make a copy which you can save to your Google Classroom and adapt as needed for your students. These were initially created for 4/5 grade level students but are helpful in providing basic background information for middle school grades too.
Lesson 1-What is renewable energy?
Lesson 2-What is nonrenewable energy?
Suggested Videos:
What is Climate Change and What Can We Do? (6:46)
Temperature Record 101: How we know what we know about climate change (8:41)
Causes and Effects of Climate Change (for students) (3:04)
5 Things You Need to Know About Climate Change (for students) (1:05)
How Global Warming Works (for teachers) (4:44)
Tour a Wind Turbine (4:23)
How do wind turbines work? (5:02)
Suggested Curriculum:
National Energy Education Department (NEED)
Vermont Energy Education Program (VEEP)
Suggested Vocabulary:
English/Spanish Vocabulary List (PDF)
Biomass Energy- Comes from anything that is alive such as trees, crops, garbage, and animal waste, and can be converted to heat to produce electricity.
Carbon Dioxide- A colorless, odorless noncombustible gas with the formula CO2 that is present in the atmosphere. It is formed by the combustion of carbon and carbon compounds (such as fossil fuels and biomass) and by respiration, which is a slow combustion in animals and plants, and by the gradual oxidation of organic matter in the soil.
Clean Energy- Also known as renewable energy which does not emit carbon dioxide.
Climate Change- Is when there is a big difference in normal climate patterns over a long time (30 years or more).
Climate Justice- Is a term and a social movement that acknowledges climate change can have disproportionately harmful, social, economic, and public health impacts on marginalized or otherwise vulnerable populations.
Coal- Is a sedimentary rock formed hundreds of millions of years ago when plants died, were buried, and under heat and pressure changed into coal. Today, coal is burned to produce electricity.
Fossil Fuel- Fuels (coal, oil, natural gas, etc.) that result from the compression of ancient plant and animal life formed over millions of years.
Generator- A machine that converts kinetic energy into electricity.
Geothermal Energy- The heat energy that is produced by natural processes inside the earth. It can be taken from hot springs, reservoirs of hot water deep below the ground, or by breaking open the rock itself.
Greenhouse Gases- Gases that trap the heat of the sun in the Earth's atmosphere, producing the greenhouse effect. The two major greenhouse gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide. Lesser greenhouse gases include methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
Hydropower- Energy that comes from moving water.
Nonrenewable- Fuels that cannot be easily made or "renewed." We can use up nonrenewable fuels. Oil, natural gas, and coal are nonrenewable fuels.
Nuclear Energy- Energy that comes from splitting atoms of radioactive materials, such as uranium.
Natural Gas- Is a mixture of gases you can't see, smell, or taste that is found underground and can be burned to make heat used to produce electricity. It is considered a fossil fuel.
Renewable- Fuels that can be easily made or "renewed." We can never use up renewable fuels. Types of renewable fuels are hydropower (water), solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass.
Turbine- A device with blades, which is turned by a force, eg.that of wind, water, or high pressure steam. The mechanical energy of the spinning turbine is converted into electricity by a generator. a type of machine in which a wheel is driven by the movement of a liquid or gas.
Variable- things that can be changed during an experiment that affect the outcome
Dependent Variable- is what you measure in an experiment and is affected by the independent variable eg. amount of electricity (measured in Volts) produced by a turbine given a certain wind speed
Independent Variable- what is being controlled or manipulated by the experimenter eg. changing the wind speed from low to high on the fan and measuring the electricity output
Blade Pitch or Angle- the angle of the blades with respect to the plane of rotation (Blades perpendicular to the oncoming wind would be 0 degrees. Blades parallel to the wind would be 90 degrees)
Volts (V)- a measure for how much electricity is being produced by the generator
Definitions adapted from: https://www.eia.gov/kids/